![]() Print this Article
Print this Article ![]() Share with friends
Share with friends ![]() Bookmark to Favorites!
Bookmark to Favorites!
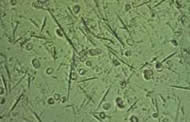
Purines: Crystals of Gout (disease)
"The gout is the result of a disorder of purine degradation which causes an accumulation of uric acid in the blood. Purines come from food (beer and shellfish especially) and help to the functioning of the cells of the body. Purines lead to the creation of urate crystals (see photo) that store in the joints, creating severe pain and deformation, essentially in the foot."
Article by: the gout
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Rate this article (4864 votes)
Rate this article (4864 votes)
What are the main purine-rich foods to avoid for gout?
To reduce gout, a low purine diet and a significant decrease in alcohol intake is desirable. Especially the beer must absolutely be stopped because it contains a very large amount of purines (beer without alcohol also).
Tea is also to be avoided because it favors the elimination of water by the body, which can cause a sudden gout disease.
Purines for 100 g
- Brewer's yeast: 5 000 mg
- Tea (dried leaves): 2 200 mg
- Cocoa: 1 200 mg
- Vegetables: 180 to 220 mg
- Meat: 80 to 120 mg
Purine, food rich in purines to avoid the gout pain
Avoid alcohol (especially beer), tea and other purine-rich food: seafood, anchovies, game meat, offal, consommés, asparagus, spinach, peas, lentils, sauces, cheese, fried foods. Learn more about the diet for the goutBrowse by Categories
About the Gout
Gout symptoms
Discover the main symptoms of gout on the body: fever, joint swelling, pain, and more.

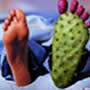
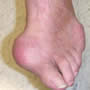
Gout toe photos
Discover surprising photos of the gout toe of the foot and other deformations: ear, hand, feet...

Gout treatment
Discover a selection of the best treatments for gout: paracetamol, colchicine, etc...
Glossary about Gout
Uric acid
Substance that is the cause of gout (if rate greater than 0,08 g/l), which is derived from the degradation of purines...
[+] Learn more about uric acid

Purines
Substance located in food (beer, anchovies, etc) which in excess cause gout. They help our DNA...

Tophus or Uric acid crystals
Clusters of uric acid crystals that cause deformation on the joints and the under the skin... 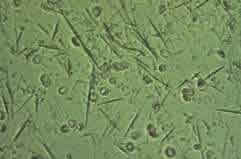

Full glossary about Gout [+] more
Allopurinol: A medical drug that is used to lower the levels of uric acid in the blood.
Drugs for gout: a medical drug that decreases the inflammation caused by gout.
Gouty arthropathy: Destruction of the joints due to tophus (cluster of uric acid crystals).
Kidney stones: « stones » mainly created in the urinary tract.
Colchicine: medical drug that relieves gout pain (also used in prevention) learn more about colchicine
Renal colic: very intense lower back pain due to "stones" that close up the urinary tract.
Hyperuricemia: uric acid rate in the blood above the normal rate (> 420 µmol/l or 70 mg/l).
Hypouricemia: medical treatment to reduce the level of uric acid in the body.
Infiltration: injection of a product directly into a joint.
Renal failure: progressive, important and definitive degeneration of the kidney function.
Psoriasis: chronic disease that affects first the skin.
 Popular:
Popular: